Whether seeking exercise or cargo-hauling convenience, trikes are a popular cycling option for many. However, with human-powered and electric-assisted models available, the choice can seem complex. This guide provides a balanced look at the key attributes of these two main trike types through comparisons of features, costs, and suitability for varied riding abilities and transportation needs. By understanding the similarities and tradeoffs between these two options, you can better determine which type of trike strikes the right balance for your lifestyle and purposes.
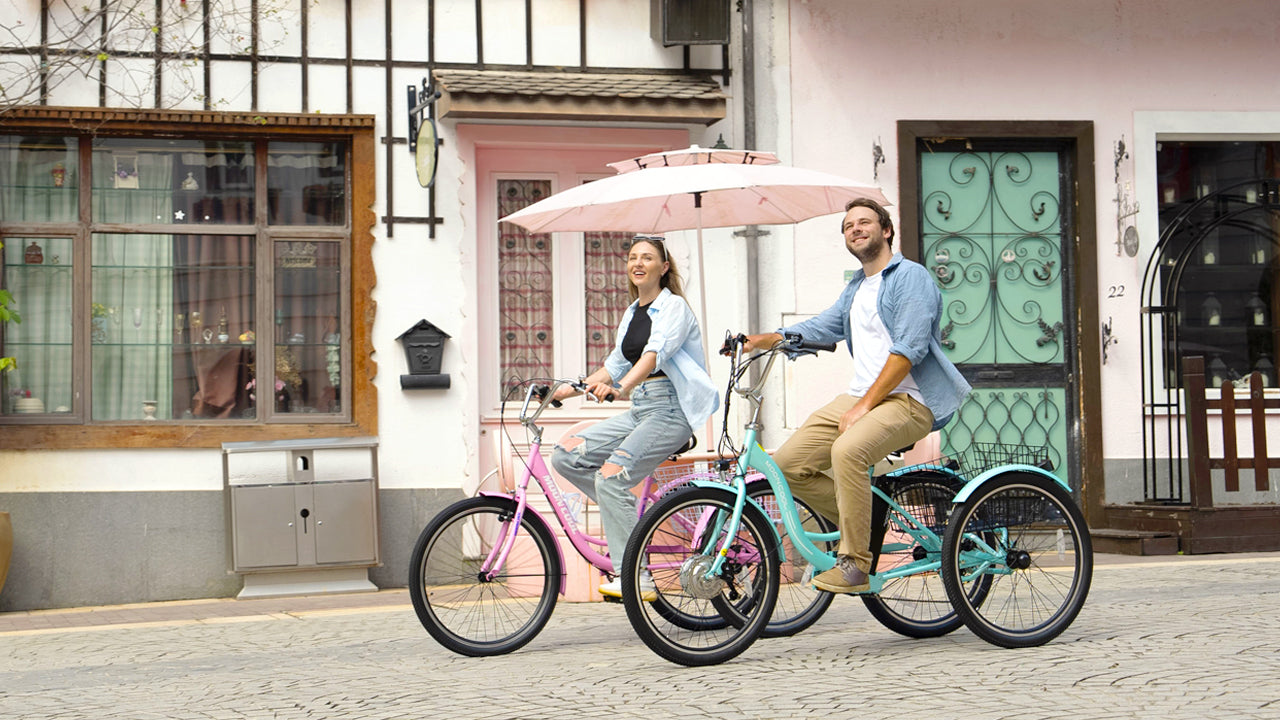
Pedal Tricycles - Key Considerations
Pedal trikes allow riders to explore at their own pace and ability level without relying on batteries. However, their limitations are important to weigh:
- The mileage range is restricted based on the rider's fitness and endurance. Covering long distances or highly strenuous routes cannot be sustained by occasional cyclists. Expect to build leg strength over time.
- Maximum speeds top out according to each person's physiology and pedaling cadence. Maintaining faster paces is unrealistic for casual riders or on hilly terrain. Don't expect to keep up with road cyclists. For a more in-depth exploration, click here: How fast can people travel, on a bicycle or tricycle. Does 20-25 km/hour sound alright?
- Daily commuting over lengthy distances or on busier roads is impractical without electric assistance. The constant pedaling required outpaces most riders' capacity. Plan routes under 5 miles.
- For some seniors or people with physical limitations, continuous pedaling may be overly taxing except on short, recreational outings close to home. Their options expand with electric models.
In summary, pedal-powered trikes excel for leisurely neighborhood riding but quickly reveal limitations for more demanding transportation or fitness training needs.
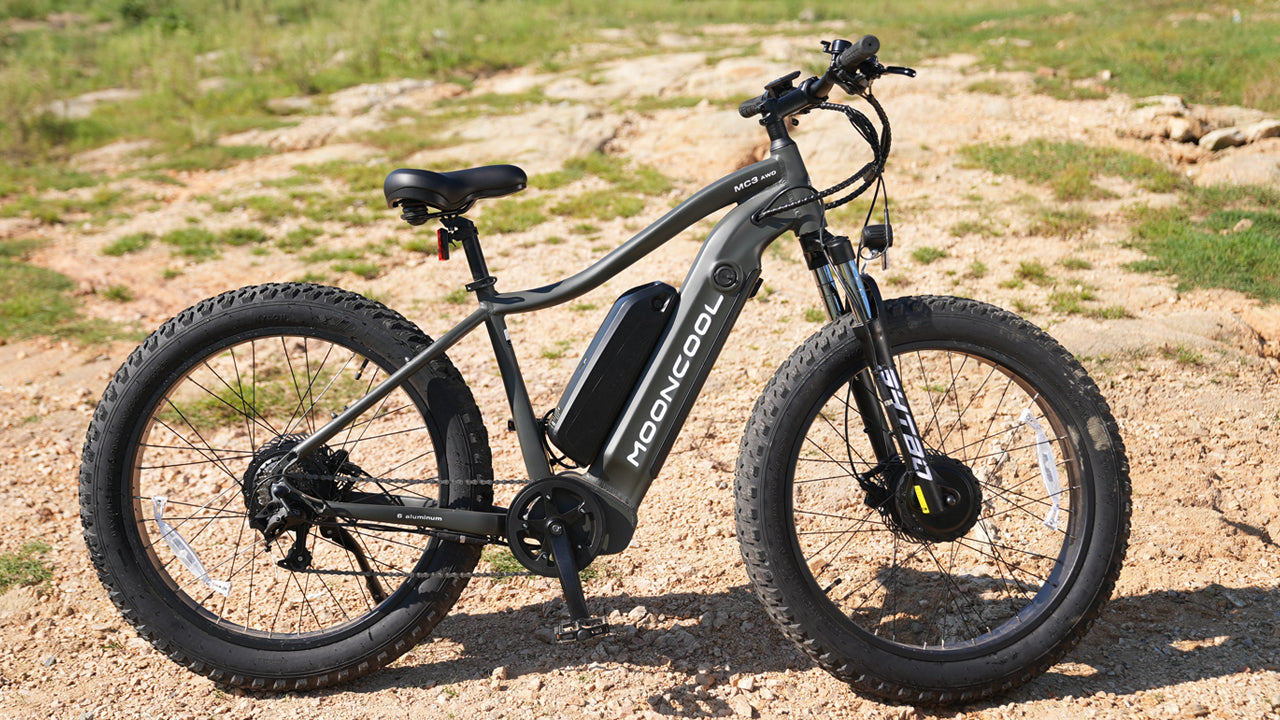
Electric Trikes - Enhanced Enjoyment
Electric trikes open cycling to a wider range of abilities thanks to their pedal-assist motors. They excel for:
- Empowering casual cyclists, seniors, and those with disabilities to ride more frequently and farther by removing barriers posed by challenging terrain or their own fitness limitations. The motor provides an adaptive boost when needed.
- Extending range during long recreational rides, bike tours, or cargo hauling. Riders can tackle hilly routes and travel up to 40 miles between battery charges thanks to supplemental motor power.
- Providing older adults with an active transportation option that preserves their independence. Seniors who otherwise might lose access to cycling due to declining mobility can continue riding assisted models.
In short, e-trikes enable diverse riders to rediscover the joys and utility of cycling by reducing physical exertion yet retaining a healthy activity level. Read to know more about e-trikes: Enjoy the Last Mile of Your Journey - Electric Trike.
Electric Trikes - Pros and Common Uses
Electric trikes expand cycling accessibility through battery-powered assistance activated by easy, intuitive controls:
- Power assist opens cycling to riders of all fitness levels. Those less physically fit can still participate and tackle challenging terrain.
- The electric motor provides an extra boost for long, comfortable rides. Trips up to 40 miles are achievable between charges.
- Hill climbing becomes more manageable. Riders can smoothly traverse hilly recreational routes or multi-day tours.
- Older adults and people with disabilities or mobility limitations can rediscover cycling's joys. The motor compensates for their physical restrictions. For further insights, click here: How Electric Trikes Empower the Disabled with Enhanced Mobility?
In summary, electric trikes empower diverse cyclists to ride farther for commuting, exercise, or recreation. The battery assist makes extended cycling trips accessible to more people.
Electric Trikes - Cons and Downsides

While convenient, electric trikes do carry some inconveniences:
- Batteries only support a limited range per charge, typically 20-40 miles, depending on terrain and assist level. Running out of juice can leave riders stranded.
- Battery maintenance introduces responsibilities like proper charging, storage, and replacement every few years. This ongoing care ensures maximum battery life. Click here to learn more: 6 STEPS FOR PROPER BATTERY MAINTENANCE.
- Recharging planning becomes necessary for intensive riders. Spontaneous trips may get disrupted by the need to plug in for extended charging sessions.
To conclude, electric trikes require battery upkeep that impacts ownership costs versus human-powered pedal designs. In addition, given that the Mooncool e-trikes can reach speeds up to 25 mph, planning your journey and charging accordingly becomes essential to avoid being stranded.
Cost Comparison
When weighing pedal against electric trikes, purchase price, and long-term operating costs help determine the better value:
- Entry-level pedal trikes start around $500-800 without suspensions or accessories. Their mechanical simplicity keeps manufacturing costs low.
- Meanwhile, basic electric trikes begin around $300-1000. The additional motor, battery, and electronic components add to the base price.
- Over an electric trike's multi-year lifespan, periodic battery replacements further increase costs. Pedal trikes avoid this, instead demanding only the rider's leg power.
- However, pedaling expends significant calories. Frequent riders require extra food to fuel their mileage, representing an overlooked expense. Electric assist reduces these dietary costs. Click to learn more: How many calories does biking burn?
In summary, while electric trikes carry higher initial price tags, their motorized support can save money over a lifetime by minimizing the impact of physical exertion. Read to know more: Ride On: How E-Trikes Help Beat Anxiety and Depression in Midlife?
Features Comparison
When evaluating electric and pedal trike models, several key features impact performance and utility:
- Controls: Pedal trikes rely solely on gear shifters and leg power to control speed and effort level. Meanwhile, electric trikes offer variable pedal assistance and throttle control to smoothly regulate electrical boosts.
- Suspension: The suspension also differs, with pedal trikes more often lacking rear suspension or having only basic front shocks. Electric trikes more commonly include front and rear suspension to handle battery weight and cushion rides.
- Use Cases: The two also diverge in ideal use cases. Pedal trikes suit recreational riding for exercise on bike paths. But electric trikes better meet needs for long-distance transportation, heavy cargo hauling, or accessibility for those with physical limitations.
By understanding these key distinctions in features, maintenance, and optimal applications, buyers can select the trike type that best aligns with their cycling purposes, abilities, and preferences.
Conclusion
Whether you value exercise freedom or transportation practicality, weighing each option's capabilities against your personal goals will lead you toward the best cycling experience. Don't just take my word for it - try test-riding different models to feel the difference human or battery power can make. Reflect on how far you realistically expect to ride and what type of terrain you may encounter. Also, think about any cargo needs or physical limitations that could impact your mobility.
By gaining hands-on insight and critically assessing your individual situation, you'll be empowered to choose the trike with features that truly let you shine on two wheels, regardless of ability level. The joys of cycling await - will human muscle or battery boosts be your passionate means of discovery?



Leave a Comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.